High Voltage Insulator
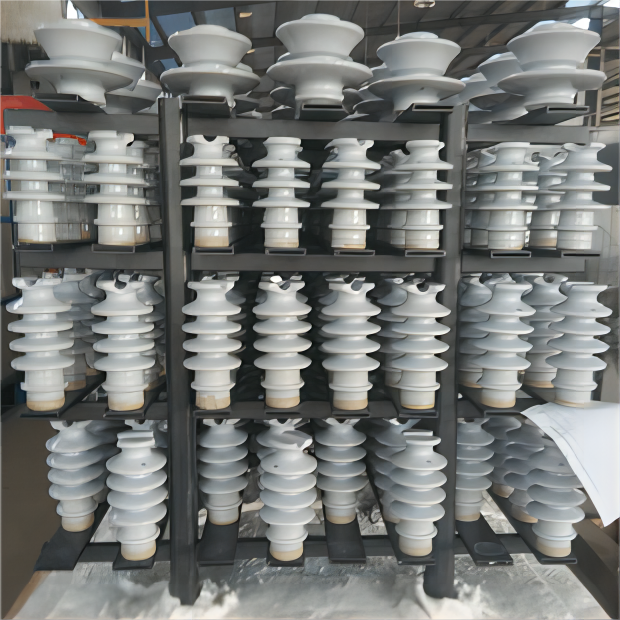
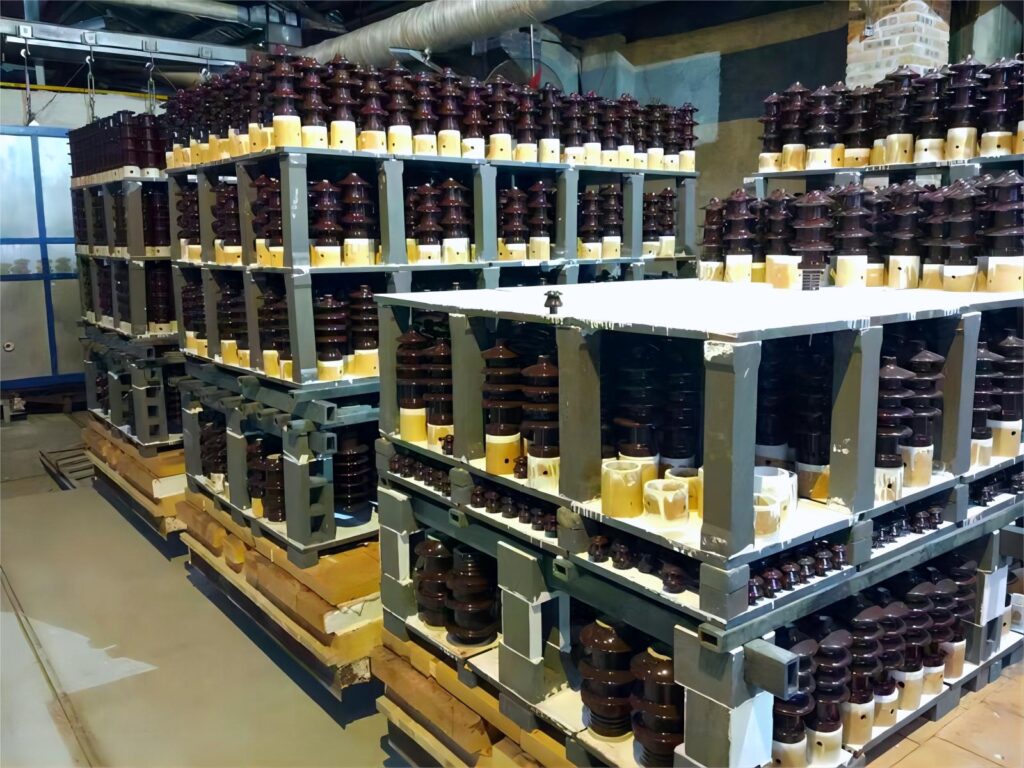
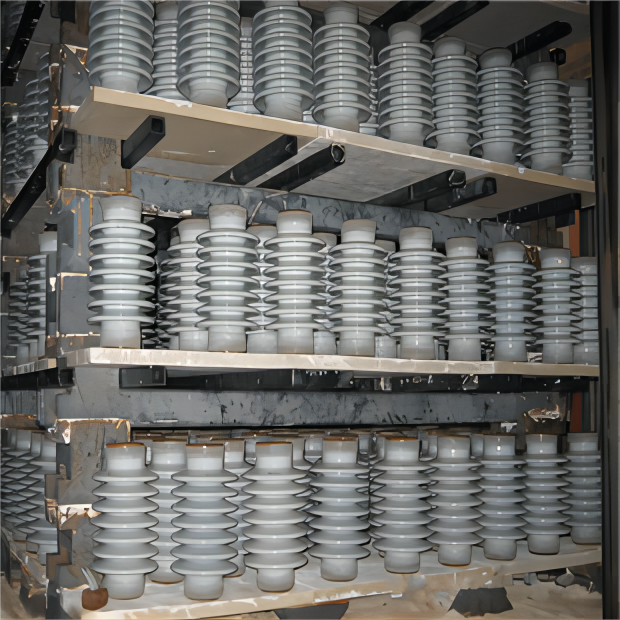


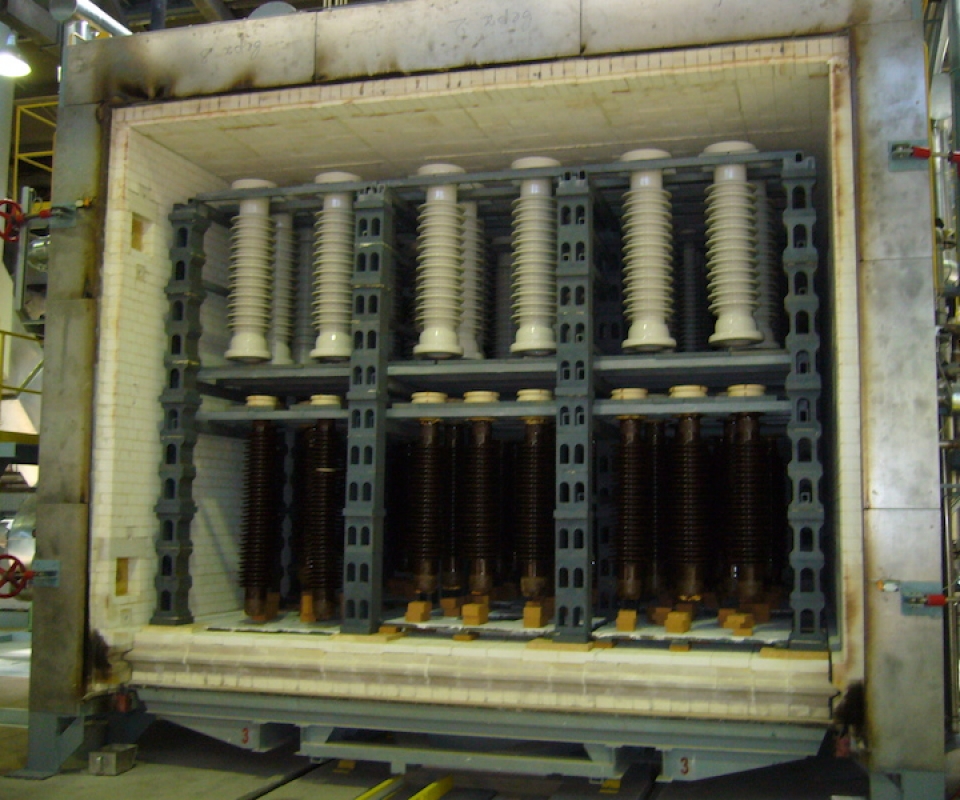

High voltage insulators are specialized components designed to electrically isolate and mechanically support conductors in high voltage power systems. They are typically manufactured from porcelain, glass, or composite polymers, all of which possess excellent dielectric strength and mechanical durability.
The primary role of these insulators is to prevent the unintended flow of electric current between energized conductors and grounded structures, thereby ensuring safe and reliable operation in power transmission and distribution networks.
For porcelain insulators, the firing temperature during manufacturing generally ranges from 2200°F to 2500°F (1200°C to 1370°C). This high-temperature sintering process is crucial for achieving the necessary mechanical strength, density, and electrical insulation performance.
logo-300x127.png)